TortoiseCVS |
TortoiseCVS is now recommended as the preferred method for using CVS on Windows, replacing WinCVS. TortoiseCVS has several advantages in that it:
- Integrates directly into windows explorer.
- Provides more functionality.
- Does not require that you use an insecure ssh key with no pass phrase.
TortoiseCVS does not enable you to:
- Issue CVS commands from GoGui.
- Issue CVS commands from the command line.
Also see WinCVS.
Note: To do either of the above, requires that you have WinCVS functionality.
Prerequisites
This procedure assumes that you have already installed:
- Kerberos
- PuTTY
If you have not, please refer to Secure Shell (SSH) for Windows, and install them now.
Install TortoiseCVS
- Download and install a free copy of TortoiseCVS.
Note: A User's Guide is included with the download.
- To setup the TortoiseCVS Preferences, go to Start --> Programs --> TortoiseCVS --> Preferences and make sure the settings are as shown below.
Notes:
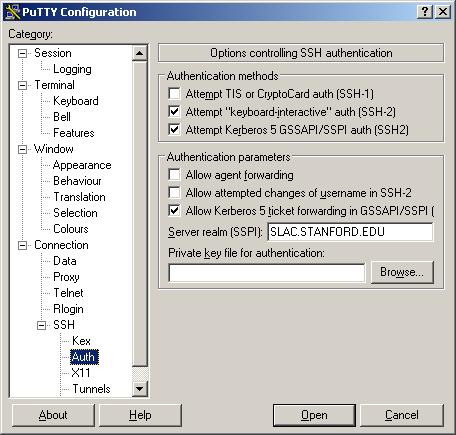
- This step assumes that the C:\Program Files\Putty-GSSAPI\plink.exe is the correct path for your installation; if it is not the correct path, be sure to adjust it accordingly.
- Don't forget to add the -g under SSH parameters, which tells it to use Kerberos for login.
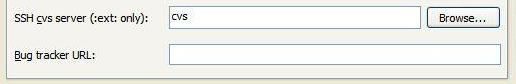
Note: Later version(s) of Tortoise CVS have two additional fields (SSH cvs server (:ext:only): and Bug tracker URL:) These fields can be left at their default values as shown below:
-
If you already have some code checked out from CVS, open that folder (in which the code is stored) in explorer and observe that TortoiseCVS has added:
- New icons to all the files to show their status.
- New items to the popup context menus for all files and folders.
All normal CVS commands can now be performed directly from windows explorer.
- If you want to checkout a new module from CVS:
- Navigate to a folder on your local drive that you want the code placed in, and open it.
- Right click within the folder or, from the explorer's File menu, select CVS checkout.
- Using the values below as a guide, fill in the form, then click OK to check-out the new module.
- Be sure that you are logged in to the Kerberos Network ID Manager for the day (see Logging in to Kerberos).
- Set up a PuTTY session on centaurusa.slac.stanford.edu and Save it.
The following screen captures show the proper configuration for a PuTTY session (refer as necessary to Secure Shell (SSH) for Windows):
a. Connection --> SSH --> Authentication
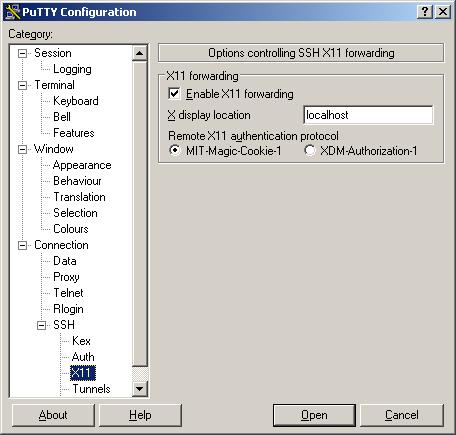
b. Connection --> SSH --> X11
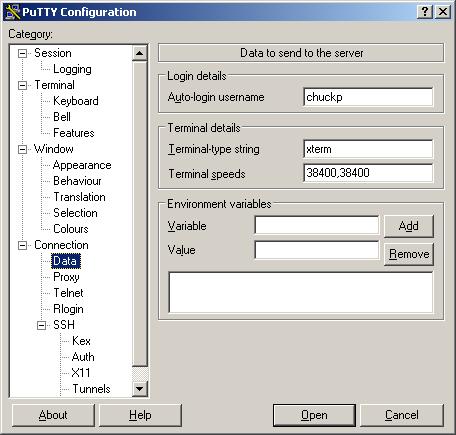
c. Connection --> Data
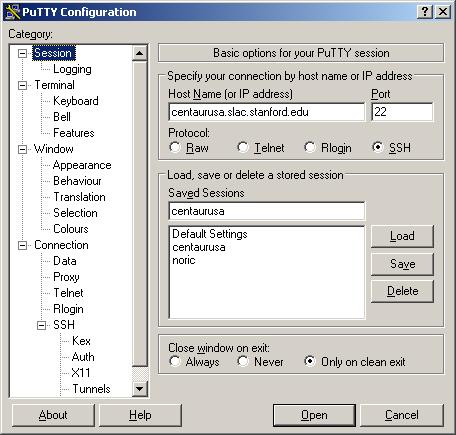
d. Session
Note: Observe that the Host Name is: centaurusa.slac.stanford.edu
(all lowercase!) .Tip: Don't forget to enter the Saved Session name (e.g., centaurusa) before
clicking on the Save button.e. Click on the Open button to start a session on centaurusa.
You should not be required to enter a password.
Troubleshooting: If a password is required, launch the Kerberos Network Identity Manager and get a new token.
- Use TortoiseCVS to perform a CVS operation.
You should not have to give your password.
Tip: If you are unable to perform a CVS operation:
- Load the Centaurusa session.
- Save the session as glastlnx07.
- Click on the Open button.
- Try performing a CVS operation.
Useful CVS References:
Owned by: Tony Johnson
| Last updated by: Chuck Patterson 03/03/2011 |