simDetector.adl
simDetector is a driver for a simulated area detector. The simulation detector is useful as a model for writing real detector drivers. It is also very useful for testing plugins and channel access clients.
This driver inherits from ADDriver. It implements nearly all of the parameters in asynNDArrayDriver.h and in ADArrayDriver.h, with the exception of the file saving parameters, which it does not implement. It also implements a few parameters that are specific to the simulation detector. The simDetector class documentation describes this class in detail.
The writeInt32 and writeFloat64 methods override those in the base class. The driver takes action when new parameters are passed via those interfaces. For example, the ADAcquire parameter (on the asynInt32 interface) is used to turn acquisition (i.e. computing new images) on and off.
The simulation driver-specific parameters are the following:
| Parameter Definitions in simDetector.cpp and EPICS Record Definitions in simDetector.template | ||||||
| Parameter index variable | asyn interface | Access | Description | drvInfo string | EPICS record name | EPICS record type |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SimGainX | asynFloat64 | r/w | Gain in the X direction | SIM_GAINX |
$(P)$(R)GainX $(P)$(R)GainX_RBV |
ao ai |
| SimGainY | asynFloat64 | r/w | Gain in the Y direction | SIM_GAINY |
$(P)$(R)GainY $(P)$(R)GainY_RBV |
ao ai |
| SimGainRed | asynFloat64 | r/w | Gain of the red channel | SIM_GAIN_RED |
$(P)$(R)GainRed $(P)$(R)GainRed_RBV |
ao ai |
| SimGainGreen | asynFloat64 | r/w | Gain of the green channel | SIM_GAIN_GREEN |
$(P)$(R)GainGreen $(P)$(R)GainGreen_RBV |
ao ai |
| SimGainBlue | asynFloat64 | r/w | Gain of the blue channel | SIM_GAIN_BLUE |
$(P)$(R)GainBlue $(P)$(R)GainBlue_RBV |
ao ai |
| SimResetImage | asynInt32 | r/w | Set to 1 to reset image back to initial conditions | RESET_IMAGE |
$(P)$(R)Reset $(P)$(R)Reset_RBV |
longout longin |
| SimImageType | asynInt32 | r/w |
Set the image type to be displayed. Options are:
|
SIM_IMAGE_TYPE |
$(P)$(R)ImageType $(P)$(R)ImageType_RBV |
longout longin |
| SimNoise | asynInt32 | r/w |
Used to introduce randomness. Each affected pixel is assigned a scaling factor. scalingFactor = 1.0 + (rand()%noise +1)/100.0 |
SIM_NOISE |
$(P)$(R)Noise $(P)$(R)Noise_RBV |
longout longin |
| Parameters for Peak Array | ||||||
| SimPeaksStartX | asynInt32 | r/w | X location of the first peak centroid | SIM_PEAK_START_X |
$(P)$(R)PeakStartX $(P)$(R)PeakStartX_RBV |
longout longin |
| SimPeaksStartY | asynInt32 | r/w | Y location of the first peak centroid | SIM_PEAK_START_Y |
$(P)$(R)PeakStartY $(P)$(R)PeakStartY_RBV |
longout longin |
| SimPeaksWidthX | asynInt32 | r/w | X width of the peaks | SIM_PEAK_WIDTH_X |
$(P)$(R)PeakWidthX $(P)$(R)PeakWidthX_RBV |
longout longin |
| SimPeaksWidthY | asynInt32 | r/w | Y width of the peaks | SIM_PEAK_WIDTH_Y |
$(P)$(R)PeakWidthY $(P)$(R)PeakWidthY_RBV |
longout longin |
| SimPeaksNumX | asynInt32 | r/w | Number of peaks in X direction | SIM_PEAK_NUM_X |
$(P)$(R)PeakNumX $(P)$(R)PeakNumX_RBV |
longout longin |
| SimPeaksNumY | asynInt32 | r/w | Number of peaks in Y direction | SIM_PEAK_NUM_Y |
$(P)$(R)PeakNumY $(P)$(R)PeakNumY_RBV |
longout longin |
| SimPeaksStepX | asynInt32 | r/w | X step between peaks | SIM_PEAK_STEP_X |
$(P)$(R)PeakStepX $(P)$(R)PeakStepX_RBV |
longout longin |
| SimPeaksStepY | asynInt32 | r/w | Y location of the first peak centroid | SIM_PEAK_STEP_Y |
$(P)$(R)PeakStepY $(P)$(R)PeakStepY_RBV |
longout longin |
| SimPeakHeightVariation | asynInt32 | r/w |
Used to introduce randomness. Each gaussian peak in the array is assigned a scaling factor. scalingFactor = 1.0 + (rand()%peakVariation +1)/100.0 |
SIM_PEAK_HEIGHT_VARIATION |
$(P)$(R)PeakVariation $(P)$(R)PeakVariation_RBV |
longout longin |
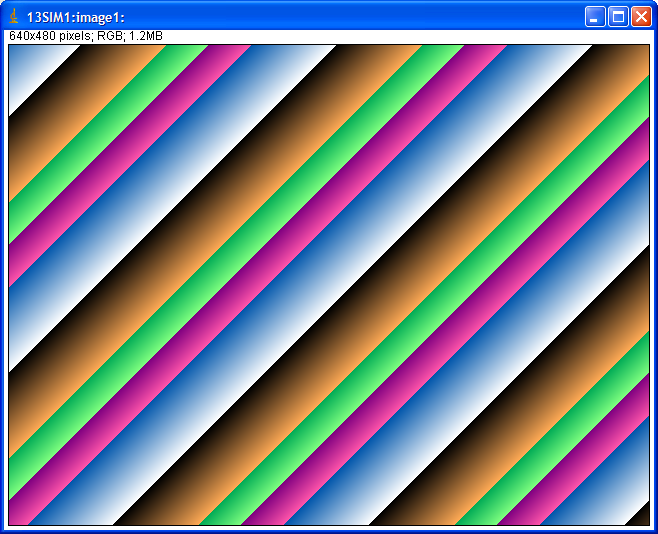
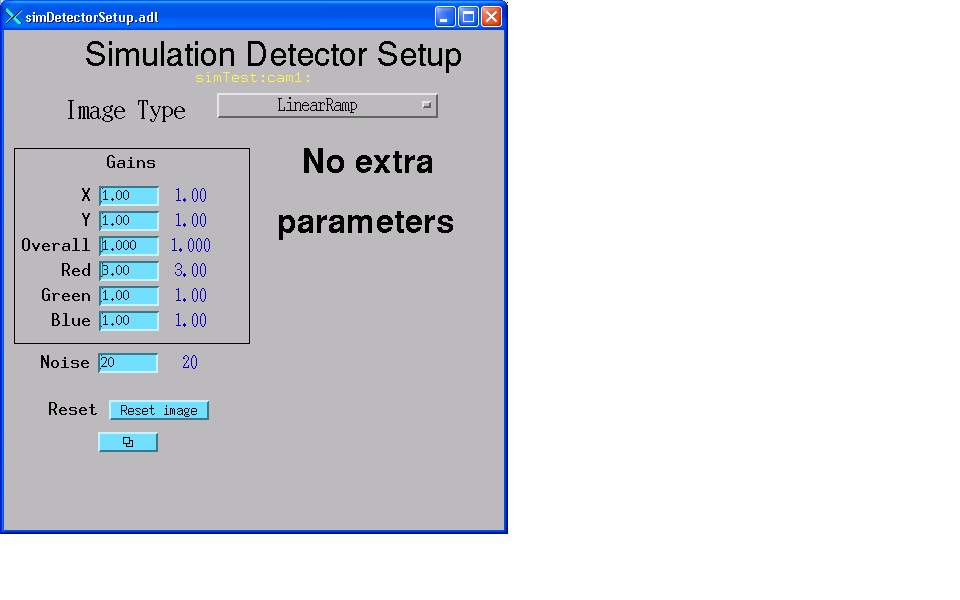
For monochrome images (NDColorMode=NDColorModeMono) the simulation driver initially sets the image[i, j] = i*SimGainX + j*SimGainY * ADGain * ADAcquireTime * 1000. Thus the image is a linear ramp in the X and Y directions, with the gains in each direction being detector-specific parameters. Each subsquent acquisition increments each pixel value by ADgain*ADAcquireTime*1000. Thus if ADGain=1 and ADAcquireTime=.001 second then the pixels are incremented by 1. If the array is an unsigned 8 or 16 bit integer then the pixels will overflow and wrap around to 0 after some period of time. This gives the appearance of bands that appear to move with time. The slope of the bands and their periodicity can be adjusted by changing the gains and acquire times.
For color images (NDColorMode=NDColorModeRGB1, RGB2 or RGB3) there are 3 images computed, one each for the red, green and blue channels. Each image is computed with the same algorithm as for the monochrome case, except each is multiplied by its appropriate gain factor (SimGainRed, SimGainGreen, SimGainBlue). Thus if each of these color gains is 1.0 the color image will be identical to the monochrome image, but if the color gains are different from each other then image will have color bands.
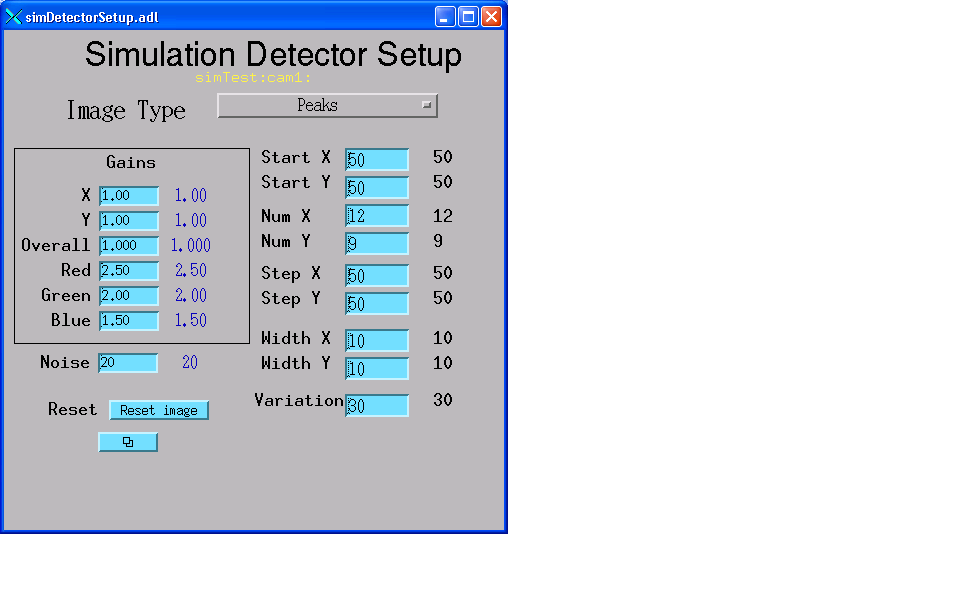
For monochrome images, an array of gaussian peaks is produced. The user specifies the start location for the first peak in PeakStartX & PeakStartY. The size of the peak is controlled by PeakWidthX and PeakWidthY. The array is specified by giving the number of peaks in each direction with PeakNumX and PeakNumY and the step size between peak centroids with PeakStepX and PeakStepY. Note that data for each peak is only added to the image over a range of four times the PeakWidth in any direction (in the interest of speed).
Dynamic behavior can be introduced into the system by changing PeakVariation and Noise records. PeakVariation introduces variation on each pixel in the array and Noise introduces variation in each pixel.
The description for RGB images is the same as for the Linear Ramp. Pixels are computed the same way as for monochrome and there is a separate gain for each color.
An array of Rings will be added later.
The simDetector driver is created with the simDetectorConfig command, either from C/C++ or from the EPICS IOC shell.
int simDetectorConfig(const char *portName,
int maxSizeX, int maxSizeY, int dataType,
int maxBuffers, size_t maxMemory,
int priority, int stackSize)
The simDetector-specific fields in this command are:
maxSizeX Maximum number of pixels in the X direction for the simulated
detector.maxSizeY Maximum number of pixels in the Y direction for the simulated
detector. dataType Initial data type of the detector data. These are the enum
values for NDDataType_t, i.e.
For details on the meaning of the other parameters to this function refer to the detailed documentation on the simDetectorConfig function in the simDetector.cpp documentation and in the documentation for the constructor for the simDetector class.
There an example IOC boot directory and startup script (iocBoot/iocSimDetector/st.cmd) provided with areaDetector.
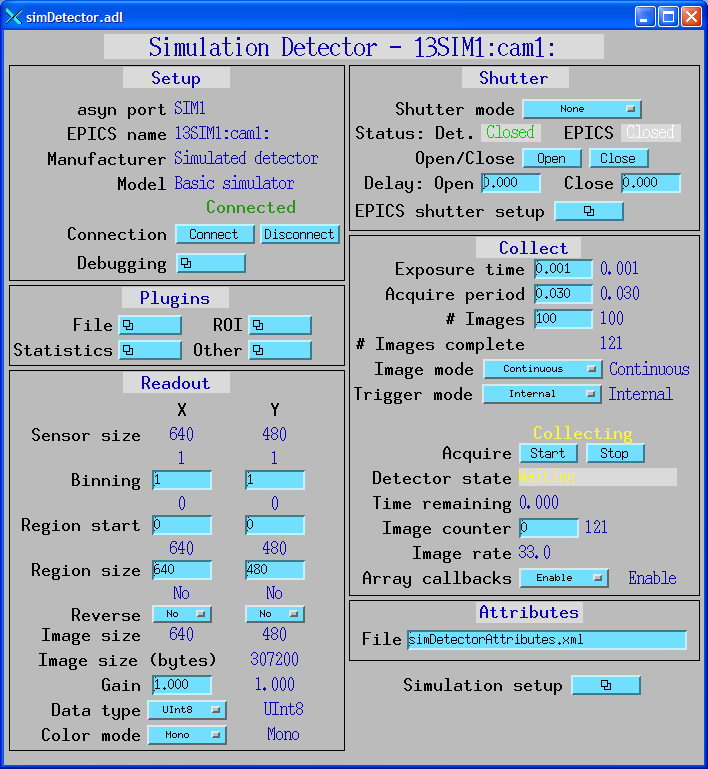
The following is the MEDM screen simDetector.adl for the simulation detector.

The following is the MEDM screen that provides access to the specific parameters for the simulation detector.
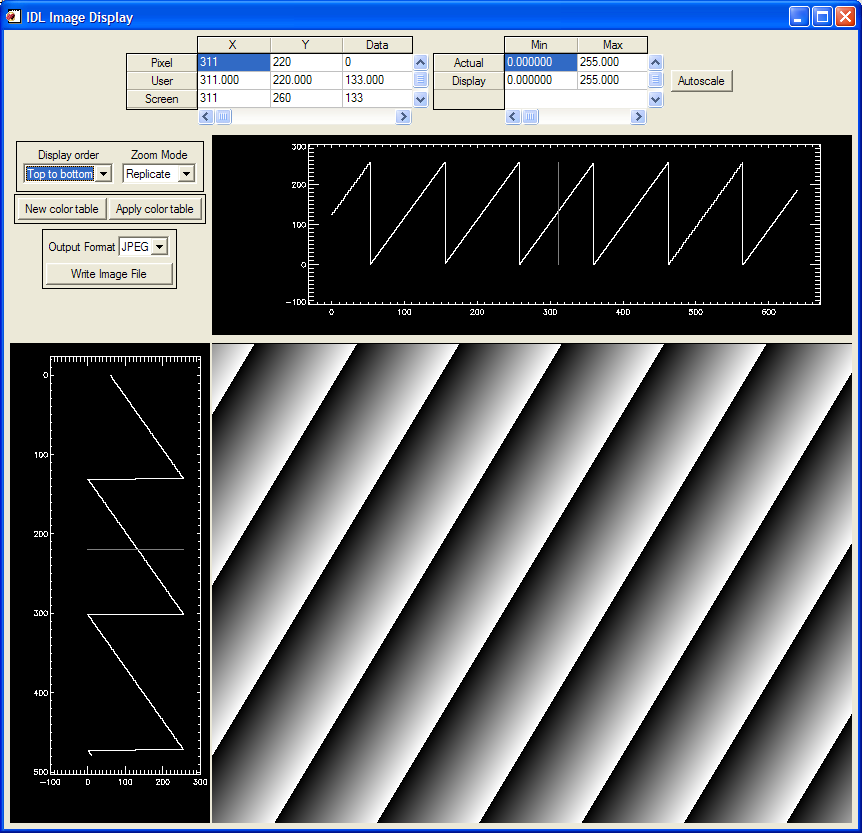
The following is an IDL epics_ad_display screen using image_display to display the simulation detector images.
The following is an ImageJ plugin EPICS_AD_Viewer screen displaying color simulation detector images.