Science Analysis Systems Software
As its name implies, the Science Analysis Systems (SAS) group is responsible for developing and maintaining the software that takes "raw" Level 0 data delivered to it in LAT Data Format (LDF data) and converts it into Level 1 data that is ready for scientific analysis. During this conversion process, event data is reconstructed and events are classified as gamma rays or charged particles.
SAS Software Releases
Each release of Science Analysis Systems software contains many different software packages, and each package is contained in a directory in the main Concurrent Versioning System (CVS) repository. Each package is also tagged, and a tag of a GlastRelease package "seals in concrete" the versions of other packages upon which that package depends. A software release is determined by the version numbers that are contained each package's Configuration Managment Tool 's requirements file, the only place that explicitly specifies the version of each package contained in a release.
Tip: In conjunction with CVS, the Configuration Management Tool (CMT) is used to manage the build of a software release. It is CMT that knows how to do a recursive checkout. MRvcmt is a frontend GUI designed to facilitate such checkouts. Though MRvcmt is the recommended method, developers using a Linux machine may also use glastpack to do recursive checkouts. (See Build Tools.)
Checkout Packages (also known as "Source Code Toolkits")
SAS software includes top-level checkout packages, applications packages, and constituent packages. An application package (e.g., GLEAM, Em1, Em2, Likelihood Analysis, etc.) has, as its sole purpose, the creation of an executable. For each of the three top-level checkout packages there is a package coordinator, responsible for promoting a specific build to release status. Source code can be obtained from the Concurrent Versions System (CVS) repository, or binary versions of any of the packages can be downloaded using the GLAST Installer.
Note: It is useful to think of the top-level packages as source code toolkits from which you can select the constituent package(s) included in the kit that you will need in order to compile and analyze event information you are interested in.
|
|
|
GlastRelease is the primary SAS software package and is a toolkit of different application software packages with a wrapper bundling them into a single package; The top-level application package within a GlastRelease is the GLast Event Analysis Machine (GLEAM). GLEAM takes the "raw" Level 0 data delivered to it in LAT Data Format (LDF data) and converts it to Level 1 data. The Level 1 data serves as input to the ScienceTools software packages. Note: All GlastRelease outputs are in ROOT format. |
|
A version of the GlastRelease toolkit modified in support of the Beam Test at CERN (to be conducted from late July through mid-September, 2006). |
|
EngineeringModels 1 & 2 (Em1 and Em2) are versions of the GlastRelease toolkit used for integration and testing. |
|
ScienceTools is a toolkit of analysis tools with a wrapper bundling it into a single package. These tools are developed and used for analysis of Level 1 data. Energies, directions, times, and other high-level characteristics of the gamma rays are used together with pointing and livetime information for the LAT to detect and characterize astrophysical sources of gamma rays. Note: Most of the ScienceTools packages are components of the Standard Analysis Environment (SAE) being developed jointly with the GLAST Science Support Center and are compatible with the FTOOLS standards. |
|
Top-level packages have shell scripts located in the bin subdirectory of the directory where the rest of the code for the top-level package is compiled. These shell scripts enable you to execute all of the executables available within the package. |
|
Constituent Packages (e.g, AcdDigi, AcdRecon, CalDigi, CalRecon, TkrDigi, TkrRecon, etc.) are specific packages included in a top-level package. |
External Libraries
When you download a checkout package using the GLAST Installer, the external libraries required for that release will be automatically included unless you specify otherwise.
External libraries used by GlastRelease software:
- ROOT
- CLHEP
- Xerces
- Gaudi
- Mysql
- GEANT4
- LDF
- CFITSIO
- HTL
- OmniOrb
- FOX
- ZLIB
External libraries used by ScienceTools software:
- ROOT
- CFITSIO
- PIL
- PYTHON
Package and External Library Contents
To view the package and external library contents of code builds, including the version number for each package, click on:
http://glast-ground.slac.stanford.edu/releasemanager/CodeReleases.jsp
TIP: Pull down menus enable you to select Package, Version, and Tag and, when you click on the Submit button, the external packages are displayed by default; to view the entire package contents of a release, click on All Packages.
Release Manager
The Release Manager software makes a build each time a new version of a package is checked in, whether for GlastRelease, BeamtestRelease, EngineeringModel, or ScienceTool software. It also runs a series of tests to ensure interoperablility with other packages that have been checked in. Developers are notified by e-mail of any test failures related to their package.
Release Manager links provide access to build logs and details of build results, including package lists, test results, errors, date, elapsed time, etc. A Summary Page is provided for each package version and links are also provided to:
- Release Notes detailing differences with respect to the previous version
- System Tests Outputs
- Doxygen Outputs
- XML Geometry Parameters
- CVSWEB View of Packages
- "Red-dot" Package Summary
- Source Code: Linux and Windows
Note: For more detailed information, see: Advanced --> Release Manager
SAS Software Builds
Optimized software builds (e.g., rh9_gcc32opt, rhel14_gcc34opt, and VC8) run significantly faster than unoptimized builds, and hence are desirable for event analysis. However, there is also the need to use a debugger during development as well as to track down bugs in production builds; hence, the need for unoptimized builds. While it would be convenient to have both optimized and unoptimized builds of everything readily available, that could quickly create an unnecessary strain on resources such as disk space, and SAS has therefore created the following build classes; each class serving a different function and having a different build frequency:
- Tagged releases (optimized and unoptimized builds)
- HEAD (unoptimized builds only)
- LATEST (unoptimized builds only)
- External Libraries:
- optimized builds of libraries heavily used during event processing (e.g., Geant and Gaudi)
- Unoptimised builds of less frequently used libraries (e.g., Xerces, used almost exclusively during initialization)
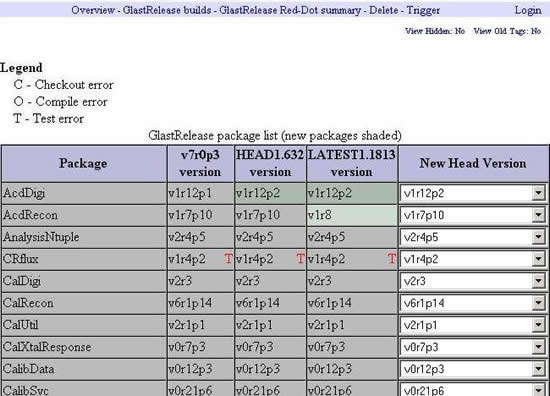
GlastRelease Red-Dot Summary
Red-Dot Summary pages are displays of packages that have changed when packages in the current release are compared with the packages in the previous release. For example, there are four columns on the GlastRelease Red-Dot Summary page:
- package name (e.g., AcdDigi)
- release(d in) specifies version, revision, and patch of the latest GlastRelease tag (i.e., a release and by definition, past history)
- HEAD specifies a candidate set of packages to be the next GlastRelease
- LATEST is a predictor of the next release; it lists the latest tag applied to a package, not necessarily the tag slated for the next release. Each of these packages is built nightly, so their state is known. As this column becomes error free, it becomes more certain that future releases will be smooth.
Note: A T indicates a package version failed one or more tests.
GLAST Software Installers
Two GLAST Software Installers are available: a GUI-based installer which can be used by Linux and Windows users, and a Linux Command Line Installer for Linux users only. These installers enable you to download and install the binaries of a top-level package (e.g., GlastRelease, BeamtestRelease, EngineeringModel, or ScienceTools), the External Libraries for those packages, the Configuration Management Tool (CMT) and the ROOT libraries (rootlibs) for GlastRelease, BeamtestRelease, or EngineeringModel.
Build Tools
In addition to GLAST Installer commands, you may also want to familiarize yourself with one the following Build Tools:
|
On the red navigation bar, see MRvcmt. |
|
(Linux only) On the red navigation bar, see:
|
Also see: |
|
|
On the red navigation bar, see FRED, the current event display tool. |
Related Topics
For additional Information on SAS Software, also see:
- IT & Tea Presentation given on May 12, 2005
| Last updated by: Chuck Patterson 01/15/2009 |